Netzsch Pump Curves: What You Need to Know
Understanding pump curves is essential for anyone involved in the selection, operation, or maintenance of pumps. Netzsch, a leader in the pump industry, provides comprehensive pump curves that serve as crucial tools in ensuring optimal performance. This article will explore the significance of Netzsch pump curves, their components, and how to interpret them effectively.
What Are Pump Curves?
Pump curves are graphical representations that illustrate the relationship between a pump’s flow rate and its head, which is the height to which the pump can raise a fluid. Netzsch pump curves specifically provide insights into the performance characteristics of their pumps, allowing users to make informed decisions based on their unique applications.
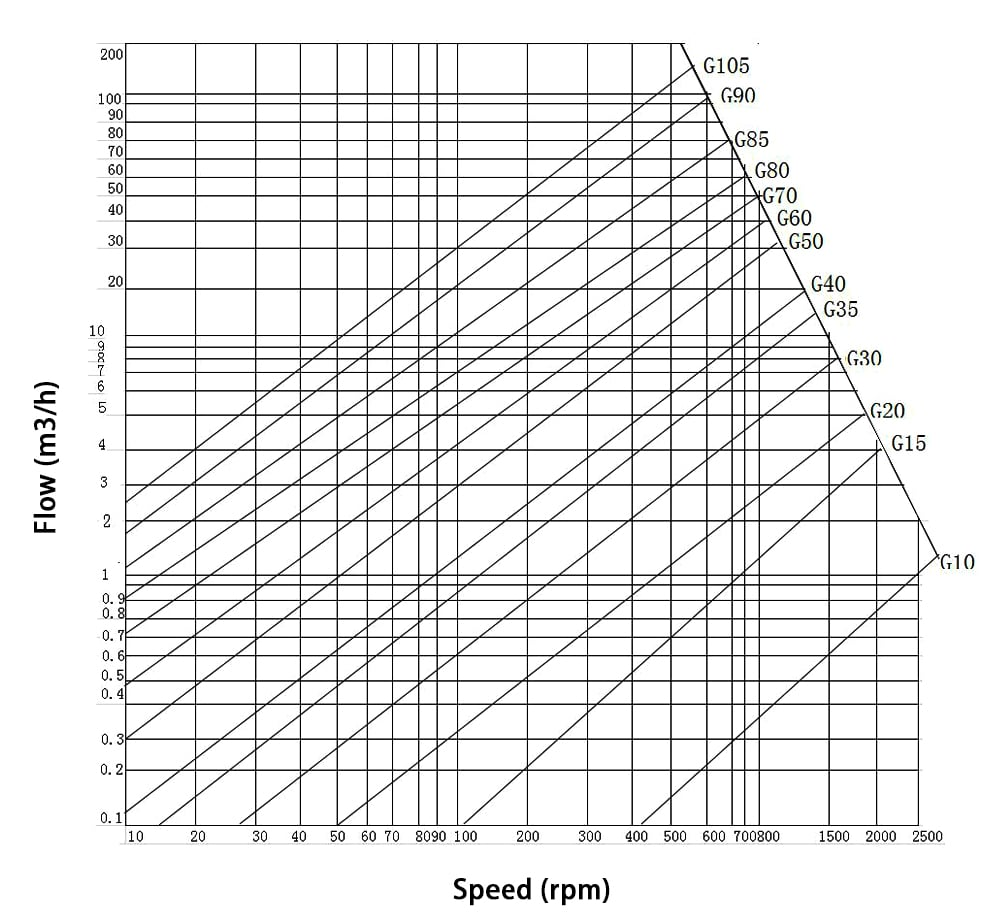
Why Are Netzsch Pump Curves Important?
- Performance Assessment: Netzsch pump curves help assess how well a pump will perform under specific operating conditions. By analyzing these curves, users can determine the efficiency and effectiveness of a pump for their particular needs.
- System Compatibility: Understanding pump curves allows engineers to ensure that a selected pump will operate harmoniously within a given system. This compatibility is vital for preventing issues such as cavitation or excessive wear.
- Energy Efficiency: By selecting pumps based on their curves, users can optimize energy consumption, leading to lower operational costs. This is especially important in industries where energy expenses are significant.
Key Components of Netzsch Pump Curves
When examining Netzsch pump curves, several components are essential to understand:
- Flow Rate: This is the volume of fluid that the pump can move over a specified time. It is typically represented on the horizontal axis of the curve.
- Head: The head indicates the energy imparted to the fluid by the pump and is usually shown on the vertical axis. It reflects the height to which the pump can elevate the fluid.
- Efficiency: Many pump curves include efficiency lines that show how effectively a pump converts input power into hydraulic energy. Higher efficiency means lower energy costs.
- NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head): This aspect is critical for preventing cavitation, which can damage pumps. The curve demonstrates the minimum NPSH required for reliable operation.
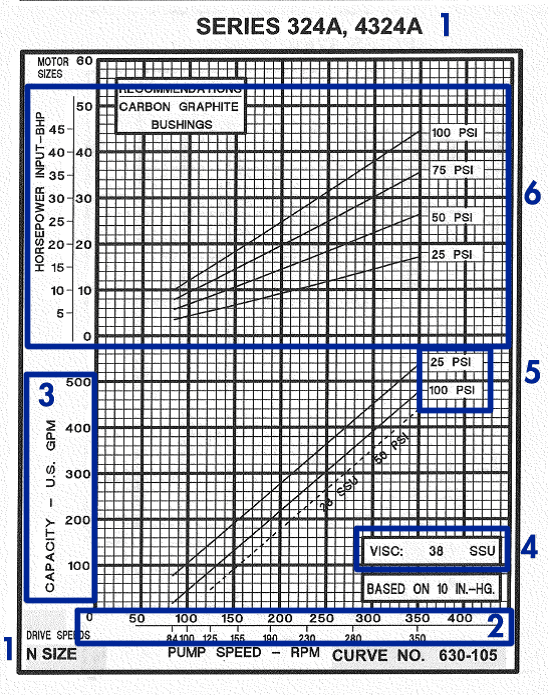
How to Interpret Netzsch Pump Curves
Interpreting Netzsch pump curves involves several steps:
- Identify Operating Conditions: Determine the required flow rate and head for your application.
- Locate the Point on the Curve: Find the point on the curve that corresponds to your operating conditions. This will indicate the pump’s expected performance.
- Check Efficiency: Look at the efficiency lines to ensure the pump operates within an efficient range for your application.
- Evaluate NPSH: Ensure that the available NPSH in your system meets or exceeds the required NPSH indicated on the curve.
Conclusion
Netzsch pump curves are invaluable tools that provide critical insights into pump performance and compatibility. By understanding these curves, engineers and operators can make informed decisions that enhance system efficiency and reliability. Whether you are selecting a new pump or evaluating an existing one, taking the time to analyze Netzsch pump curves will ultimately lead to better operational outcomes.




